
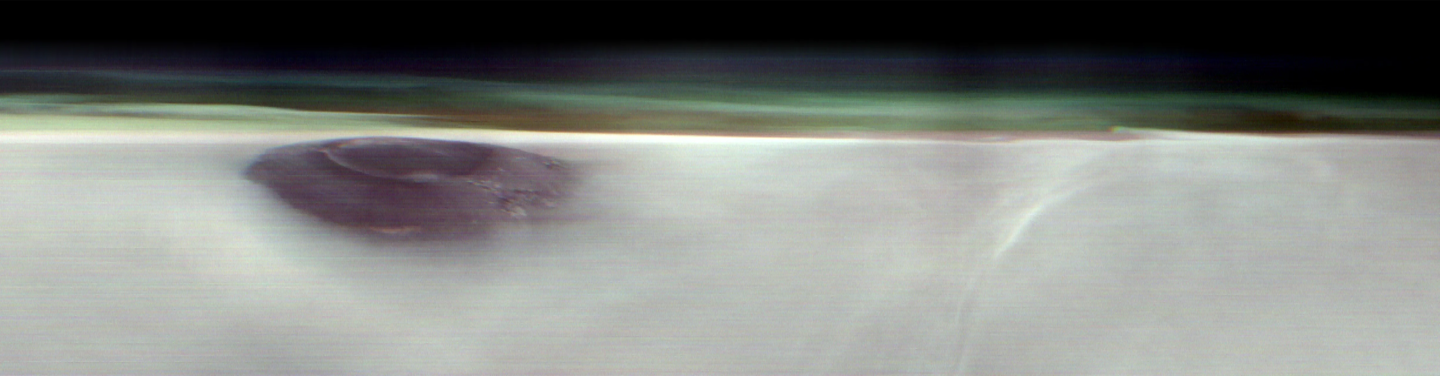
 在6月8日的新闻中,美国宇航局昨天宣布,火星奥德赛轨道轨道拍摄了一张历史悠久的照片,清楚地记录了巨大的火星阿西亚·蒙斯(Mars Arsia Mons)在黎明前浸渍云层的罕见场景。这张照片是在5月2日拍摄的,阿尔西亚峰火山的上部逐渐从云层出现。他寻求公共信息,发现火山约为12英里(约20公里),其高度是君主的两倍,君主是地球上最高的火山(大约6英里/9公里高)。这是人类第一次就行星地平线拍摄火山景观,模拟宇航员观察角,并从国际空间站景观。这种历史记录引起了广泛的关注,尤其是在大气和地质研究领域。 “这些Horizon Reve Imageslan的主要季节性差异,并提供了研究的新线索来研究atmosphere of Mars, "says Michael Smith, a planetary scientist at the NASA's Goddard Space Center. The shooting is the fourth result of the Odyssey great altitude image program since he launched the Mars Horizon high altitude image program in 2023. To acquire images, the torque torn Record the clouds of dust and water from the Atian Marciano, which allows a chamber of images of thermal radiation (Themis). of Mars. The result was exciting “ Themis会议厅的运营总监Dijo Jonathon Hill。自2001年推出以来,奥德赛一直是最长的长期星际轨道任务。Themiscamera可以通过红外带检测Mars的地下水冰区域,还可以分析Phobo和Demos的表面组成。相关的大气数据包括火星,沙暴机制的气象模式,研究未来的着陆任务非常有价值。
在6月8日的新闻中,美国宇航局昨天宣布,火星奥德赛轨道轨道拍摄了一张历史悠久的照片,清楚地记录了巨大的火星阿西亚·蒙斯(Mars Arsia Mons)在黎明前浸渍云层的罕见场景。这张照片是在5月2日拍摄的,阿尔西亚峰火山的上部逐渐从云层出现。他寻求公共信息,发现火山约为12英里(约20公里),其高度是君主的两倍,君主是地球上最高的火山(大约6英里/9公里高)。这是人类第一次就行星地平线拍摄火山景观,模拟宇航员观察角,并从国际空间站景观。这种历史记录引起了广泛的关注,尤其是在大气和地质研究领域。 “这些Horizon Reve Imageslan的主要季节性差异,并提供了研究的新线索来研究atmosphere of Mars, "says Michael Smith, a planetary scientist at the NASA's Goddard Space Center. The shooting is the fourth result of the Odyssey great altitude image program since he launched the Mars Horizon high altitude image program in 2023. To acquire images, the torque torn Record the clouds of dust and water from the Atian Marciano, which allows a chamber of images of thermal radiation (Themis). of Mars. The result was exciting “ Themis会议厅的运营总监Dijo Jonathon Hill。自2001年推出以来,奥德赛一直是最长的长期星际轨道任务。Themiscamera可以通过红外带检测Mars的地下水冰区域,还可以分析Phobo和Demos的表面组成。相关的大气数据包括火星,沙暴机制的气象模式,研究未来的着陆任务非常有价值。